Introduction
Tablet are a popular and widely used dosage form in the pharmaceutical industry. They are solid dosage forms that contain a specific amount of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) along with excipients. Tablet are designed to be taken orally, dissolving or disintegrating in the gastrointestinal tract to release the API.
Table of Contents
What are Tablets?
They are solid dosage forms that contain a specific amount of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) along with excipients. They are designed to be taken orally, dissolving or disintegrating in the gastrointestinal tract to release the API.
Types of Tablet
There are several types of tablets, including:
- Immediate-release tablet: Designed to release the API quickly, often within 30 minutes to an hour.
- Sustained-release tablet: Designed to release the API over a longer period, often 8-12 hours.
- Controlled-release tablet: Designed to release the API at a specific rate, often over 24 hours or more.
- Extended-release tablet: Designed to release the API over an extended period, often 12-24 hours.
Advantages of Tablet
Tablet offer several advantages, including:
- Convenience: Easy to administer and transport.
- Cost-effective: Often less expensive to produce than other dosage forms.
- Precise dosing: Allows for precise control over the amount of API delivered.
- Patient compliance: Easy to take, improving patient compliance.
Manufacturing Process
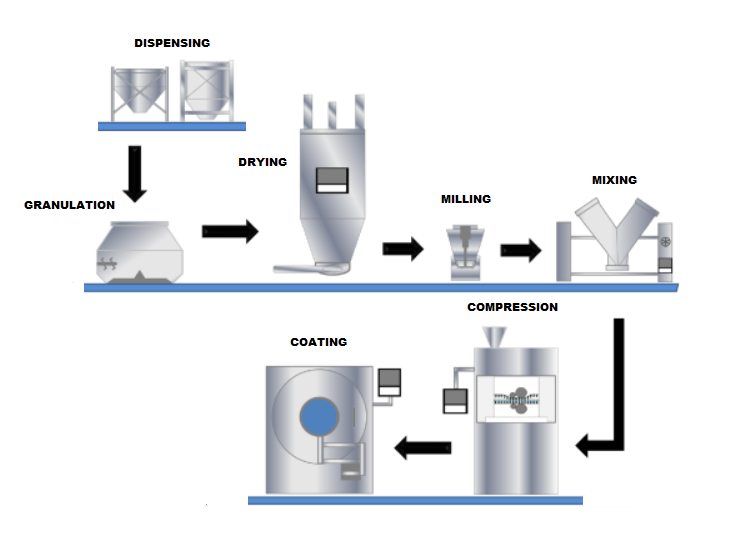
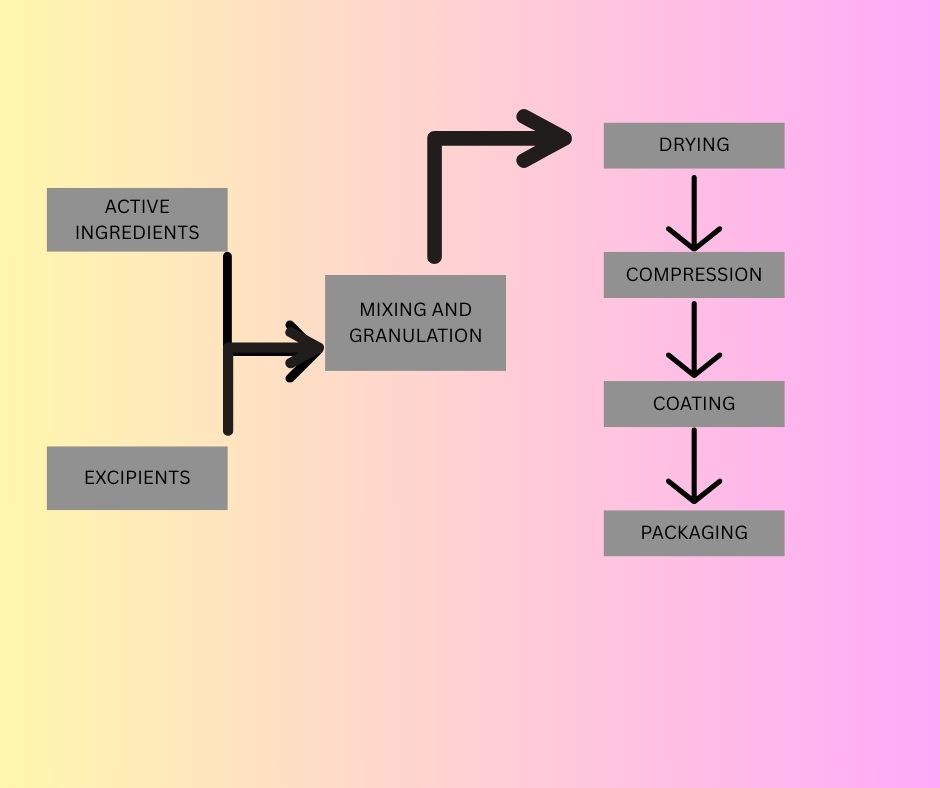
The manufacturing process for tablets involves several steps, including:
- Granulation: Mixing the API with excipients to create a uniform blend.
- Compression: Compressing the blend into tablets using a tablet press.
- Coating: Applying a coating to the tablets to improve appearance, taste, or stability.
Quality Control
Quality control is critical in tablet manufacturing, ensuring that the tablet meet the required standards for quality, safety, and efficacy. This includes testing for:
- Content uniformity: Ensuring the API is evenly distributed throughout the tablets.
- Dissolution: Ensuring the tablets dissolve or disintegrate as intended.
- Hardness: Ensuring the tablets are hard enough to withstand handling and storage.
Challenges in Tablet Manufacturing
Despite the advantages of tablets, there are several challenges in tablet manufacturing, including:
- API properties: The properties of the API can affect the manufacturability and performance of the tablets.
- Excipient selection: The selection of excipients can impact the stability, bioavailability, and efficacy of the tablets.
- Scale-up: Scaling up the manufacturing process can be challenging, requiring careful control of process parameters.
Future of Tablet
The future of tablets is exciting, with advances in technology and materials science enabling the development of:
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring tablets to individual patient needs.
- 3D printing: Creating complex tablet structures with precise control over release rates.
- Novel excipients: Developing new excipients that improve tablet stability, bioavailability, or patient compliance.
Innovations in Tablet Technology
There are several innovations in tablet technology, including:
- Orally disintegrating tablet: Tablet that disintegrate quickly in the mouth, improving patient compliance.
- Floating tablet: Tablet that float on the surface of the stomach, prolonging the release of the API.
- Bioadhesive tablet: Tablet that adhere to the mucous membranes, improving the bioavailability of the API.
Conclusion
Tablets are a popular and convenient dosage form, widely used to deliver a variety of medications. The manufacturing process for tablet involves several steps, including granulation, compression, and coating. Quality control is critical in tablet manufacturing, ensuring that the tablet meet the required standards for quality, safety, and efficacy. With advances in technology and materials science, the future of tablet is exciting, enabling the development of personalized medicine, 3D printing, and novel excipients.
References
- FDA guidelines: Guidelines for tablet manufacturing, including requirements for quality control and validation.
- Pharmaceutical research: Research articles on tablet technology, including innovations in excipients, coating, and manufacturing processes.
- Industry reports: Reports on the tablet manufacturing industry, including trends, challenges, and opportunities.

