Pellets: A Comprehensive Overview for Pharmaceutical Applications
Table of Contents
Introduction:
Pellets are small, solid dosage forms used in pharmaceuticals for oral administration. They have gained popularity due to their advantages over traditional dosage forms, such as tablets and capsules. Pellets offer improved bioavailability, controlled release, and reduced side effects, making them an attractive option for pharmaceutical manufacturers.
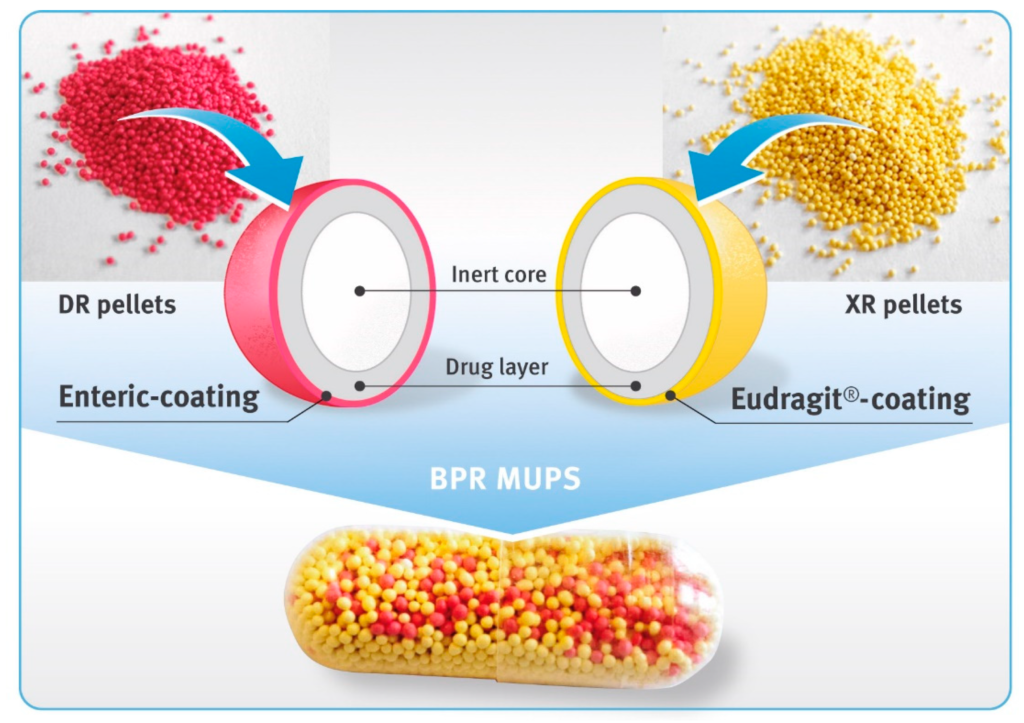
Formulation Requirements:
The formulation of pellets requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API): The therapeutic substance that provides the desired pharmacological effect.
- Excipients: Inactive ingredients that aid in the formulation and manufacture of pellet. Common excipients include binders, disintegrants, fillers, and lubricants.
- Size and Shape: Uniformity in pellet size and shape is crucial for consistent release profiles and bioavailability.
Pelletization Process:
The pelletization process involves several techniques, including:
- Extrusion-Spheronization: A process that involves mixing the API and excipients, followed by extrusion and spheronization to create uniform pellet.
- Spray Drying: A technique that involves spraying a solution or suspension of the API and excipients into a hot gas stream, resulting in the formation of pellet.
- Fluid Bed Processing: A process that involves coating or granulating the API using a fluid bed processor.
Equipments for Manufacture of Pellets:
The manufacture of pellet requires specialized equipment, including:
- Extruders: Machines that create uniform pellet shapes through extrusion.
- Spheronizers: Equipment that shapes and rounds pellets to achieve uniform size and shape.
- Fluid Bed Processors: Machines that coat or granulate the API using a fluid bed process.
- Spray Dryers: Equipment that creates pellets through spray drying techniques.
Benefits of Pellets:
Pellet offer several benefits over traditional dosage forms, including:

- Improved Patient Compliance: Pellet can be formulated to provide convenient dosing regimens, improving patient compliance.
- Enhanced Bioavailability: Pellet can be designed to improve the bioavailability of APIs, resulting in better therapeutic outcomes.
- Controlled Release: Pellet can be formulated to provide controlled release profiles, allowing for sustained or extended release of the API.
Applications:
Pellets have a wide range of applications in pharmaceuticals, including:
- Oral Drug Delivery: Pellet can be used to deliver APIs orally, providing controlled release profiles and improved bioavailability.
- Modified Release Formulations: Pellet can be formulated to provide modified release profiles, allowing for tailored therapeutic outcomes.
Advantages of Pellets:
Pellets offer several advantages over traditional dosage forms, including:
- Flexibility in Formulation: Pellet can be formulated to provide a wide range of release profiles and bioavailability.
- Improved Stability: Pellet can be designed to improve the stability of APIs, reducing degradation and improving shelf life.
- Reduced Side Effects: Pellet can be formulated to reduce side effects by providing controlled release profiles and minimizing peak plasma concentrations.
Challenges in Pellet Formulation:
Despite the advantages of pellets, there are several challenges associated with their formulation, including:
- Uniformity: Achieving uniformity in pellet size and shape can be challenging.
- Content Uniformity: Ensuring content uniformity of the API in each pellet can be difficult.
- Scalability: Scaling up pellet production while maintaining uniformity and content uniformity can be challenging.
Conclusion:
They are a versatile dosage form that offers several advantages over traditional dosage forms. With careful consideration of formulation requirements, pelletization process, and equipment, pellet can be designed to provide controlled release profiles and improved bioavailability. While there are challenges associated with pellet formulation, the benefits of pellets make them an attractive option for pharmaceutical manufacturers.


