Ophthalmic Preparations
Introduction
Table of Contents

Ophthalmic preparations are pharmaceutical products designed for application to the eyes to treat various ocular conditions. These preparations must be sterile, non-irritating, and effective in delivering the active ingredient to the target site. Ophthalmic preparations come in various forms, including eye drops, eye ointments, and eye lotions, each with its own unique characteristics and requirements.
Formulation Considerations
When formulating ophthalmic preparations, several factors must be considered:
- Sterility: Ophthalmic preparations must be sterile to prevent contamination and infection.
- pH and buffering: The pH of the preparation should be close to the natural pH of the eye (around 7.4) to minimize irritation.
- Tonicity: The preparation should be isotonic with tears to prevent irritation and discomfort.
- Viscosity: The viscosity of the preparation can affect the residence time and bioavailability of the active ingredient.
- Preservatives: Preservatives may be added to prevent microbial growth, but they should be chosen carefully to avoid irritation.
Formulation of Eye Drops
Eye drops are a common type of ophthalmic preparation. They are typically formulated as:
- Solutions: Aqueous or oily solutions of the active ingredient.
- Suspensions: Suspensions of the active ingredient in a suitable vehicle.
- Emulsions: Emulsions of oil and water that can improve solubility and bioavailability.
Eye drops can be formulated with various ingredients, such as:
- Active ingredients: Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, or other medications.
- Preservatives: Benzalkonium chloride or other preservatives to prevent microbial growth.
- Buffers: Phosphate or borate buffers to maintain pH.
Formulation of Eye Ointments
Eye ointments are semi-solid preparations that provide a longer residence time and increased bioavailability of the active ingredient. They are typically formulated as:
- Ointment bases: Petrolatum or other suitable bases that provide a smooth, non-irritating texture.
- Active ingredients: Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, or other medications.
Eye ointments can be formulated with various ingredients, such as:
- Lanolin: To improve spreadability and emollience.
- Mineral oil: To improve lubrication and comfort.
Formulation of Eye Lotions
Eye lotions are aqueous solutions used to cleanse and soothe the eyes. They are typically formulated as:
- Isotonic solutions: Solutions that are isotonic with tears to prevent irritation.
- Buffered solutions: Solutions buffered to maintain a pH close to the natural pH of the eye.
Eye lotions can be formulated with various ingredients, such as:
- Saline: To provide a gentle, non-irritating solution.
- Boric acid: To provide antimicrobial activity.
Methods of Preparation
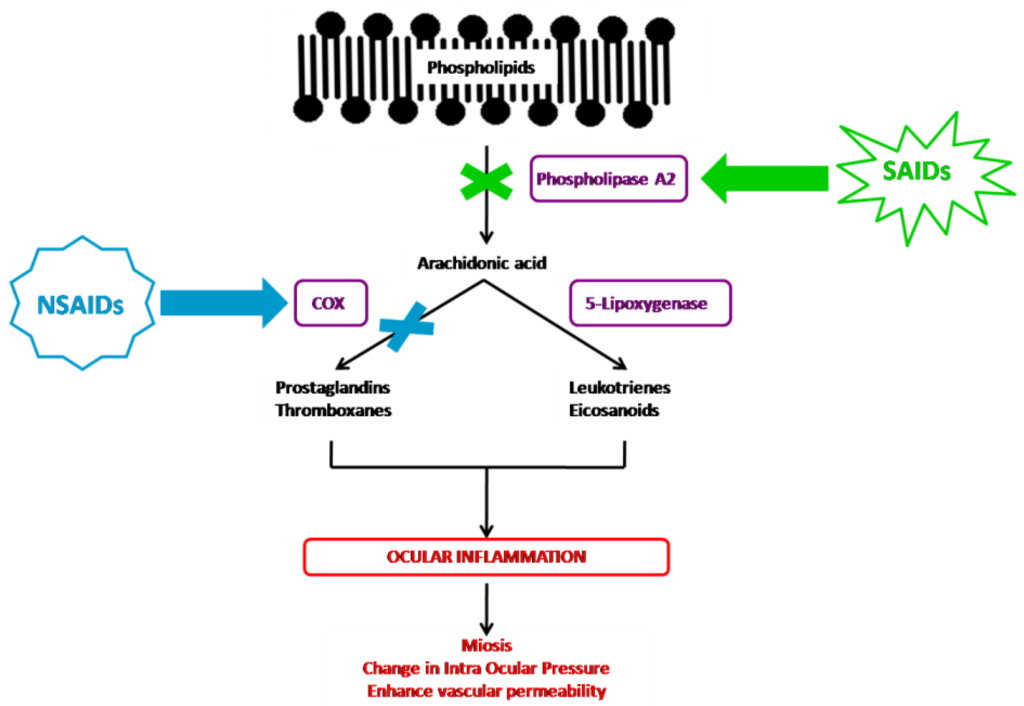
Ophthalmic preparations are typically prepared using:
- Aseptic technique: Techniques that prevent contamination and ensure sterility.
- Sterilization methods: Methods such as autoclaving, filtration, or gamma radiation to ensure sterility.
- Cleanroom facilities: Facilities that provide a controlled environment for preparation.
Labeling and Containers
Ophthalmic preparations must be labeled and packaged in a way that ensures:
- Sterility: Containers should be sterile and airtight to prevent contamination.
- Labeling: Labels should include the name of the product, active ingredient, and instructions for use.
- Tamper-evident packaging: Packaging that prevents tampering and ensures the integrity of the product.
Evaluation of Ophthalmic Preparations
Ophthalmic preparations are evaluated for:
- Sterility: Testing for sterility to ensure the preparation is free from microorganisms.
- pH and tonicity: Testing for pH and tonicity to ensure the preparation is non-irritating.
- Viscosity: Testing for viscosity to ensure the preparation has the desired consistency.
- Efficacy: Testing for efficacy to ensure the preparation delivers the active ingredient effectively.
- Stability: Testing for stability to ensure the preparation remains effective over time.
Some common tests used to evaluate ophthalmic preparations include:
- Sterility testing: Testing for the presence of microorganisms.
- pH testing: Testing for the pH of the preparation.
- Osmolality testing: Testing for the osmolality of the preparation.
- Viscosity testing: Testing for the viscosity of the preparation.
- In vitro testing: Testing for the release of the active ingredient.
In conclusion, ophthalmic preparations require careful formulation, preparation, and evaluation to ensure they are safe, effective, and non-irritating. By understanding the unique characteristics and requirements of ophthalmic preparations, manufacturers can develop high-quality products that meet the needs of patients and healthcare professionals.
- What is the primary purpose of ophthalmic preparations?
A) To treat skin conditions
B) To treat eye conditions
C) To treat respiratory conditions
D) To treat gastrointestinal conditions
Answer: B) To treat eye conditions
- Which of the following is a type of ophthalmic preparation?
A) Eye drops
B) Ear drops
C) Nasal sprays
D) Oral tablets
Answer: A) Eye drops
- What is the importance of sterility in ophthalmic preparations?
A) To prevent contamination and infection
B) To improve efficacy
C) To reduce cost
D) To increase shelf life
Answer: A) To prevent contamination and infection
- Which of the following ingredients is commonly used as a preservative in ophthalmic preparations?
A) Benzalkonium chloride
B) Sodium chloride
C) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose
D) Polyethylene glycol
Answer: A) Benzalkonium chloride
- What is the purpose of buffers in ophthalmic preparations?
A) To maintain pH
B) To increase viscosity
C) To improve efficacy
D) To reduce toxicity
Answer: A) To maintain pH
- Which of the following ophthalmic preparations provides a longer residence time and increased bioavailability of the active ingredient?
A) Eye drops
B) Eye ointments
C) Eye lotions
D) Eye washes
Answer: B) Eye ointments

