Introduction
Liquid orals dosage forms are a popular choice for many medications, offering ease of administration and flexibility in dosing. In this post, we’ll explore the formulation and manufacturing considerations for liquid orals, including syrups, elixirs, suspensions, and emulsions. We’ll also discuss filling and packaging, evaluation of liquid orals, and official pharmacopoeia standards.

Table of Contents
Formulation Considerations
When formulating liquid orals, several factors must be considered, including:
- Solubility: Ensuring the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is soluble in the vehicle. This can be achieved through the use of solvents, co-solvents, and surfactants.
- Stability: Ensuring the API remains stable in the liquid formulation over time. This can be achieved through the use of stabilizers, antioxidants, and pH control.
- Taste and palatability: Ensuring the liquid oral is pleasant to take. This can be achieved through the use of sweeteners, flavorings, and taste-masking agents.
- Viscosity: Ensuring the liquid oral has the desired viscosity for ease of administration. This can be achieved through the use of thickeners and viscosity modifiers.
Syrups
- Definition: A concentrated solution of sugar or other sweeteners, often used to mask unpleasant tastes.
- Formulation considerations: Syrups require careful consideration of sugar concentration, viscosity, and microbial stability.
- Manufacturing considerations: Syrups require precise control over temperature and mixing to ensure uniform dissolution of sugars.
Elixirs

- Definition: Hydroalcoholic solutions that can be used to solubilize APIs.
- Formulation considerations: Elixirs require careful consideration of alcohol content, pH, and stability.
- Manufacturing considerations: Elixirs require precise control over mixing and filling to ensure uniform distribution of the API.
Suspensions

- Definition: A dispersion of solid particles in a liquid vehicle.
- Formulation considerations: Suspensions require careful consideration of particle size, sedimentation, and redispersibility.
- Manufacturing considerations: Suspensions require precise control over mixing and filling to ensure uniform distribution of the API.
Emulsions
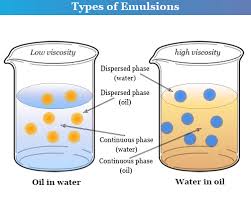
- Definition: A mixture of two or more liquids that don’t normally mix, like oil and water.
- Formulation considerations: Emulsions require careful consideration of stability, droplet size, and phase separation.
- Manufacturing considerations: Emulsions require precise control over mixing and filling to ensure uniform distribution of the API.
Filling and Packaging
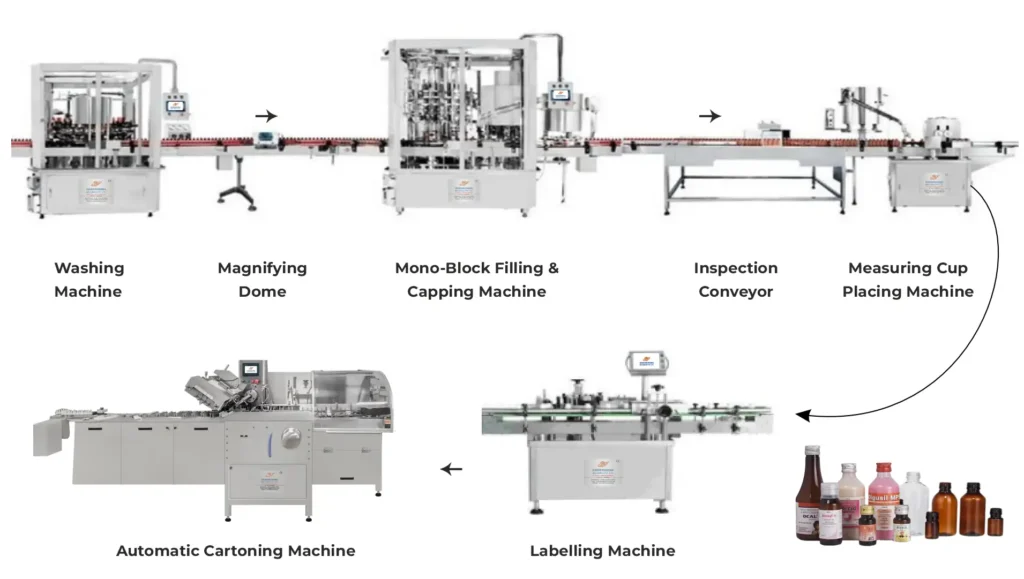
- Filling: Ensuring accurate and precise filling of liquid orals into containers. This includes considerations for fill volume, container size, and closure integrity.
- Packaging: Selecting the right packaging materials and containers for stability and compatibility. This includes considerations for container material, size, and closure system.
Evaluation of Liquid Orals
- Official pharmacopoeia standards: Ensuring compliance with official standards for quality, safety, and efficacy.
- Testing: Conducting tests for appearance, assay, pH, viscosity, and stability.
- In-process controls: Conducting controls during manufacturing to ensure the product meets quality standards.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Stability and degradation: Ensuring the API remains stable over time and doesn’t degrade into toxic compounds.
- Taste and palatability: Ensuring the liquid oral is pleasant to take and doesn’t have unpleasant side effects.
- Patient compliance: Ensuring patients take the medication as directed and don’t experience difficulties with administration.
Conclusion
Liquid orals offer many benefits, including ease of administration and flexibility in dosing. However, they also present several challenges, including stability, taste, and patient compliance. By understanding the formulation and manufacturing considerations for liquid orals, pharmaceutical manufacturers can ensure the production of high-quality products that meet official standards and patient needs.
Pharmacopoeia Standards
The official pharmacopoeia standards for liquid orals include:
- USP/NF: United States Pharmacopeia/National Formulary standards for quality, safety, and efficacy.
- EP: European Pharmacopoeia standards for quality, safety, and efficacy.
- JP: Japanese Pharmacopoeia standards for quality, safety, and efficacy.
Future Directions
The future of liquid orals is exciting, with advances in technology and materials science enabling the development of:
- Novel delivery systems: New delivery systems that improve bioavailability, stability, and patient compliance.
- Taste-masking technologies: New technologies that mask unpleasant tastes and improve patient compliance.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring liquid orals to individual patient needs and improving treatment outcomes.
By staying at the forefront of liquid oral technology and formulation, pharmaceutical manufacturers can ensure the development of safe, effective, and high-quality products that meet patient needs and improve treatment outcomes.
References

