Cosmetics: Formulation and Preparation
Table of Contents
Introduction of cosmetics
Cosmetics are products used to enhance or alter the appearance of the face or body. They are an integral part of our daily lives, playing a significant role in personal grooming, self-expression, and confidence-boosting. Cosmetics come in various forms, including skincare products, makeup, haircare products, and fragrances.
Types of Cosmetics:
- Skincare products: Moisturizers, serums, cleansers, and masks that help to nourish, protect, and improve the health of the skin.
- Makeup: Products like foundation, eyeshadow, mascara, and lipstick that enhance or alter the appearance of the face.
- Haircare products: Shampoos, conditioners, styling products, and hair dyes that help to cleanse, nourish, and style the hair.
- Fragrances: Perfumes, colognes, and scented products that provide a pleasant aroma.
Importance of Cosmetics:
- Self-expression: Cosmetics allow individuals to express their personal style and creativity.
- Confidence-boosting: Cosmetics can help individuals feel more confident and self-assured.
- Social and cultural significance: Cosmetics have played a significant role in various cultures and societies throughout history.
Lipsticks
Lipstick can be fundamentally described as a mixture of coloring agents suspended in a base made up of an appropriate combination of oils, fats, and waxes, along with suitable fragrances and flavors, shaped into sticks to provide an appealing gloss and hue when applied to the lips.

- Formulation:
- Waxes (e.g., beeswax, carnauba wax, candelilla wax)
- Oils (e.g., castor oil, coconut oil, sweet almond oil)
- Pigments (e.g., iron oxides, titanium dioxide, carmine)
- Emollients (e.g., moisturizing agents like hyaluronic acid, glycerin)
- Antioxidants (e.g., vitamin E, BHT)
- Preparation:
- Weigh and mix the waxes and oils in a heat-resistant container.
- Heat the mixture until the waxes are fully melted.
- Add the pigments and emollients to the mixture and stir well.
- Continue heating the mixture until it reaches the desired temperature (usually around 70-80°C).
- Remove the mixture from the heat and let it cool slightly.
- Pour the mixture into lipstick molds and allow it to cool and solidify.
- Once solidified, remove the lipsticks from the molds and package them for use.
Shampoos
A shampoo is a hair care product used to clean and nourish the hair and scalp. It’s typically a liquid or gel-like substance that is applied to the hair, lathered, and then rinsed out to remove dirt, oil, and other impurities.
Shampoos usually contain:
- Surfactants: to remove dirt and oil
- Moisturizers: to hydrate and soften hair
- pH balancers: to maintain a healthy scalp pH
- Formulation:
- Surfactants (e.g., sodium lauryl sulfate, cocamidopropyl betaine)
- Foaming agents (e.g., cocamidopropyl betaine, sodium laureth sulfate)
- Conditioning agents (e.g., dimethicone, panthenol)
- Preservatives (e.g., formaldehyde, parabens)
- pH adjusters (e.g., citric acid, sodium hydroxide)
- Preparation:
- Weigh and mix the surfactants, foaming agents, and conditioning agents in a large tank.
- Add the preservatives and pH adjusters to the mixture and stir well.
- Mix the ingredients together until they are fully incorporated.
- Fill the shampoo mixture into bottles or other containers.
- Label and package the shampoo for use.
Cold Creams and Vanishing Creams

- Formulation:
- Fats (e.g., beeswax, petroleum jelly)
- Oils (e.g., mineral oil, sweet almond oil)
- Water
- Emollients (e.g., glycerin, panthenol)
- Preservatives (e.g., formaldehyde, parabens)
- Preparation:
- Weigh and mix the fats and oils in a heat-resistant container.
- Heat the mixture until the fats are fully melted.
- Add the water and emollients to the mixture and stir well.
- Continue heating the mixture until it reaches the desired temperature (usually around 70-80°C).
- Remove the mixture from the heat and let it cool slightly.
- Pour the mixture into jars or tubes and allow it to cool and solidify.
- Once solidified, label and package the cream for use.
Toothpastes
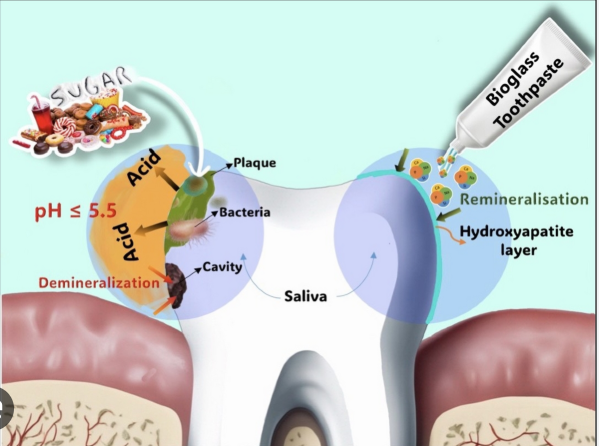
- Formulation:
- Abrasives (e.g., silica, calcium carbonate)
- Detergents (e.g., sodium lauryl sulfate)
- Fluoride (e.g., sodium fluoride)
- Preservatives (e.g., formaldehyde, parabens)
- Humectants (e.g., glycerin, sorbitol)
- Preparation:
- Weigh and mix the abrasives, detergents, fluoride, and preservatives in a large tank.
- Add the humectants to the mixture and stir well.
- Mix the ingredients together until they are fully incorporated.
- Fill the toothpaste mixture into tubes.
- Label and package the toothpaste for use.
Hair Dyes
- Formulation:
- Pigments (e.g., paraphenylenediamine, dihydroxybenzene)
- Developers (e.g., hydrogen peroxide)
- Alkaline agents (e.g., ammonia)
- Conditioners (e.g., dimethicone, panthenol)
- Preparation:
- Weigh and mix the pigments, developers, and alkaline agents in a well-ventilated area.
- Mix the ingredients together until they are fully incorporated.
- Apply the hair dye mixture to the hair.
- Allow the mixture to process for the recommended amount of time.
- Rinse the hair thoroughly with water.
Sunscreens
- Formulation:
- UV filters (e.g., oxybenzone, avobenzone)
- Moisturizers (e.g., glycerin, panthenol)
- Emollients (e.g., oils, silicones)
- Preservatives (e.g., formaldehyde, parabens)
- Preparation:
- Weigh and mix the UV filters, moisturizers,


